
Dreadlocks are matted ropes of hair with deep cultural and spiritual roots, symbolizing identity, resistance, and connection to African and Rastafarian heritage, offering versatility in modern styles.
Historical Significance of Dreadlocks
Dreadlocks trace their origins to ancient India, where rishis and sadhus wore matted hair as a symbol of spiritual devotion and renunciation. In Africa, they represented strength, wisdom, and cultural identity, as seen among warrior tribes like the Maasai. The style later gained prominence in Jamaica through Rastafarianism, embodying resistance to colonialism and a reconnection with African roots. Dreadlocks became a powerful symbol of identity, spirituality, and rebellion, evolving over centuries to transcend cultural boundaries while retaining their deep historical and spiritual significance.
Cultural Associations and Symbolism
Dreadlocks hold profound cultural and symbolic meanings, often representing spirituality, identity, and resistance. Rooted in African and Rastafarian traditions, they symbolize a connection to heritage and defiance against societal norms. In India, dreadlocks are linked to spiritual devotion among sadhus and rishis. Across cultures, they signify strength, wisdom, and nonconformity, transcending mere aesthetics to embody deep cultural values and beliefs.
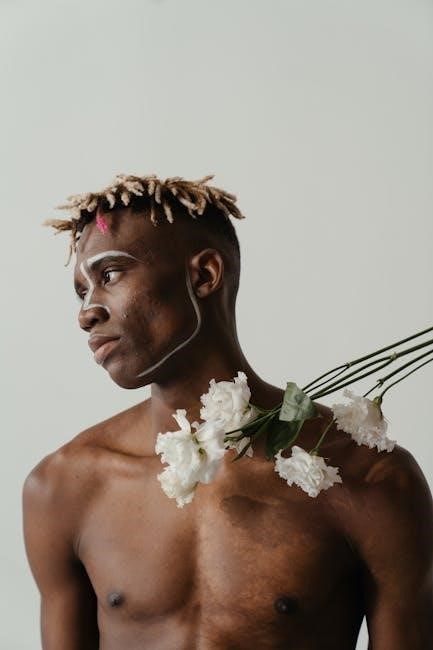

Dreadlocks in Modern Culture
Dreadlocks have evolved into a fashion statement and cultural icon, embracing diversity and self-expression. They transcend genres, appealing to musicians, artists, and individuals seeking unique identity, blending tradition with modern style.
Popularization in the 1970s and Beyond
The 1970s marked dreadlocks’ rise in global culture, linked to the Rastafarian movement and African identity. The style became a symbol of rebellion and spiritual connection, influencing music and art. By the 1980s, dreadlocks transcended their cultural origins, embraced by diverse groups worldwide. The 1990s and 2000s saw further mainstreaming, with celebrities and musicians popularizing the style. Today, dreadlocks are a staple in modern fashion, representing both cultural heritage and individuality, while continuing to evolve with contemporary trends and personal expression.
Contemporary Styles and Versatility

Dreadlocks have evolved into a highly versatile hairstyle, offering countless contemporary styles to suit diverse preferences. From sleek, uniform locs to free-form, textured designs, modern dreadlocks cater to individuality. They can be styled in updos, braids, or left loose for a natural look. Colorful dyes and decorative accessories like beads or rings add personal flair. The style’s adaptability makes it a favorite in fashion, allowing wearers to switch between casual and formal aesthetics effortlessly. Whether short or long, dreadlocks remain a dynamic choice, reflecting creativity and self-expression in today’s culture;

Caring for Dreadlocks
Regular washing, separating locs, and using natural oils are essential for maintaining healthy dreadlocks. Protecting hair at night and keeping the scalp moisturized ensures long-term vitality and strength.
Washing and Maintenance Tips
Regular washing is crucial for maintaining healthy dreadlocks. Use a mild, residue-free shampoo and warm water to cleanse the hair and scalp. After washing, rinse thoroughly and soak the locs in a mixture of apple cider vinegar and essential oils to remove impurities. Gently separate the locs to prevent matting. Avoid using heavy waxes or products that can weigh the hair down. Towel-dry thoroughly to prevent mildew and odors. For new dreadlocks, wait at least a week before the first wash to allow the hair to matt naturally. Regular maintenance ensures the locs remain clean, healthy, and well-defined over time.
Using Natural Products for Healthier Locs
Natural products are essential for maintaining healthy dreadlocks. Coconut oil and shea butter moisturize and nourish the hair, while apple cider vinegar helps balance pH levels and remove buildup. Essential oils like lavender and tea tree promote scalp health and prevent dandruff. Applying vegetable oils, such as jojoba or argan oil, softens the locs and reduces frizz. Avoid harsh chemicals and synthetic products, as they can dry out the hair. Regularly using natural products keeps the locs hydrated, shiny, and strong, enhancing their appearance and longevity. Natural care ensures the locs remain vibrant and healthy for years to come.
Social Perceptions of Dreadlocks
Dreadlocks evoke varied reactions, from cultural pride and spirituality to societal stigma. Geographical acceptance differs, with some regions embracing them while others view them as unprofessional or rebellious.
Geographical Variations in Acceptance
Geographical location significantly influences how dreadlocks are perceived. In places like Jamaica, they symbolize cultural heritage and Rastafarian identity, often celebrated as a symbol of resistance. Conversely, in regions such as South Sudan, dreadlocks are sometimes associated with negative stereotypes, linking them to unhealthy lifestyles or gang activities. In Western societies, acceptance varies, with urban areas generally embracing dreadlocks as a fashion statement while more conservative areas may view them with skepticism. These disparities highlight how cultural context shapes societal attitudes toward dreadlocks, illustrating their complex and multifaceted role across different global communities.
Dreadlocks in the Workplace and Discrimination
Dreadlocks in the workplace often face discrimination, particularly in professions with strict grooming policies. In the U.S., the EEOC has ruled that banning dreadlocks can constitute race discrimination, as they are culturally associated with African descent. However, some industries, like the military, explicitly prohibit dreadlocks, citing concerns over uniformity and safety gear fit. This has led to legal challenges, with plaintiffs arguing such bans unfairly target Black employees. Despite progress, many face workplace bias, highlighting the ongoing struggle for acceptance and the perception of dreadlocks as unprofessional in certain environments, reflecting broader societal biases against natural Black hairstyles.

Dreadlocks and Identity
Dreadlocks symbolize cultural heritage, spirituality, and resistance, deeply tied to African identity and Rastafarianism, serving as a powerful expression of self and connection to ancestral roots.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Dreadlocks hold profound psychological and emotional significance, often symbolizing empowerment, resilience, and a connection to cultural heritage. For many, they serve as a form of self-expression and identity, fostering a sense of community among wearers. However, societal stigma in certain regions can lead to emotional challenges, such as discrimination or misunderstanding. In places like Juba, dreadlocks are sometimes associated with negative stereotypes, impacting wearers’ self-esteem. Conversely, embracing dreadlocks can be a powerful act of resistance and pride, as seen in personal stories like Ghanaian rapper Amerado Burner, who linked his locs to emotional healing and cultural connection. This duality underscores their complex emotional resonance.
Dreadlocks as a Form of Resistance
Dreadlocks often serve as a powerful symbol of resistance, rejecting societal norms and embracing cultural identity. Historically tied to African and Rastafarian traditions, they represent a defiance against Eurocentric beauty standards and systemic oppression. By choosing locs, individuals assert their heritage and challenge racial stereotypes. This act of resistance is deeply personal, as seen in stories like Ghanaian rapper Amerado Burner, who linked his dreadlocks to emotional healing and cultural pride. Dreadlocks become a visual statement of resilience, rejecting assimilation and celebrating African roots, making them a potent form of resistance against cultural erasure and systemic racism.

Legal and Workplace Policies
Workplace policies often ban dreadlocks, citing grooming standards, but this raises discrimination concerns. The EEOC recognizes dreadlocks as culturally tied to African heritage, prompting legal debates.
Bans on Dreadlocks in Certain Professions
Bans on Dreadlocks in Certain Professions
Certain professions, like the military and law enforcement, often prohibit dreadlocks, citing uniformity and safety concerns. For instance, the Army’s CBRN School bans locked or braided hair, deeming it incompatible with protective gear. Similar policies exist in some corporate settings, where dreadlocks are perceived as unprofessional. These bans have sparked debates about cultural bias and racial discrimination, as dreadlocks are closely tied to African heritage. Advocates argue that such policies disproportionately affect individuals of African descent, highlighting the need for more inclusive grooming standards that respect cultural expressions while maintaining professional norms.
Legal Cases Involving Dreadlocks Discrimination
Legal battles over dreadlocks discrimination highlight racial and cultural biases. In EEOC v. Catastrophe Management Solutions, the court ruled that banning dreadlocks constitutes race discrimination, as they are culturally tied to African heritage. Similar cases, such as Robinson v. Shaklee Corp, emphasize that dreadlocks are a protected trait under anti-discrimination laws. These rulings reflect growing recognition of hair-based discrimination, aligning with the CROWN Act in some U;S. states, which prohibits bias against natural hairstyles. Courts increasingly acknowledge dreadlocks as a symbol of identity, challenging discriminatory grooming policies in workplaces and schools, fostering inclusivity and cultural acceptance in professional environments.