
Wound care certification is a vital credential for healthcare professionals, ensuring expertise in managing chronic and acute wounds. It enhances patient outcomes and advances clinical skills, providing evidence-based practices and standards for effective wound management. This certification is essential for nurses, physicians, and specialists aiming to deliver high-quality care in diverse settings.
The certification process involves rigorous study and exam preparation, focusing on key principles of wound healing, assessment techniques, and treatment methodologies. It equips professionals with the knowledge to address complex wounds, including diabetic ulcers and venous leg ulcers, while adhering to legal and ethical standards.
1.1 Understanding the Importance of Wound Care Certification
Wound care certification is crucial for healthcare professionals, ensuring expertise in managing chronic and acute wounds. It validates specialized knowledge and skills, enhancing clinical practices and patient outcomes. This credential demonstrates a commitment to evidence-based standards and continuous improvement in wound management. Certification also emphasizes the importance of accurate documentation, legal compliance, and ethical care, fostering trust and confidence in patient safety and professional integrity.
1.2 Overview of Wound Care Certification Programs
Wound care certification programs offer structured pathways for healthcare professionals to gain specialized knowledge and skills. These programs, such as the Certified Wound Care Associate (CWCA) and Certified Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse (CWOCN), provide comprehensive study guides, practice questions, and textbooks. They cover wound assessment, healing principles, and advanced management techniques, ensuring professionals are well-prepared to deliver evidence-based care and improve patient outcomes in diverse clinical settings.

Study Materials and Resources
Essential study materials include comprehensive guides, textbooks, and online courses. Practice questions and mock tests are vital for exam preparation, ensuring thorough understanding and practical application.
2.1 Essential Study Guides for Wound Care Certification
Comprehensive study guides like the CWCA Wound Care Study Guide and the Certified Wound Specialist (CWS) Home Study Guide are indispensable for certification preparation. These resources provide detailed outlines of exam content, practice questions, and annotated answers, ensuring a thorough understanding of wound care principles. Additionally, texts such as “Wound Care Certification Study Guide” by Jayesh B. Shah and “Wound Care Essentials: Practice Principles” offer evidence-based knowledge and practical case studies to aid exam success.
2.2 Recommended Textbooks and Online Courses
Key textbooks include Wound Care Certification Study Guide by Jayesh B. Shah and Wound Care Essentials: Practice Principles by Sharon Baranoski. Online courses like the WOCNCB Exam Prep Course and the Certified Wound Care Nurse (CWCN) Prep Course offer structured learning. Platforms such as the Wound Care Education Institute provide interactive modules and case studies, enhancing practical understanding and exam readiness for wound care certification.

Exam Preparation Tips
Focus on understanding key wound care concepts, practice with sample questions, and review study guides. Consider enrolling in a structured prep course to enhance readiness and confidence.
3.1 Effective Strategies for Passing the Certification Exam
Develop a structured study plan, focusing on high-yield topics like wound assessment and healing principles. Utilize practice exams to identify weak areas and refine test-taking skills. Prioritize active learning techniques, such as flashcards and case studies, to reinforce key concepts; Regularly review updated clinical guidelines to ensure familiarity with current standards. Engage in study groups or forums for collaborative learning and exam tips.
3.2 Practice Questions and Mock Tests
Engaging with practice questions and mock tests is crucial for exam success. These tools help familiarize yourself with the exam format and content, improving time management and test-taking strategies. Regularly reviewing practice questions highlights knowledge gaps, allowing targeted study. Mock tests simulate real exam conditions, building confidence and reducing anxiety. Utilize official study guides and online resources for authentic practice materials to enhance your preparedness effectively.

Key Topics in Wound Care
Key topics include wound assessment, classification, and principles of healing. Understanding tissue types, exudate, and granulation is essential. Effective management strategies and accurate documentation are also critical for optimal patient outcomes.
4.1 Wound Assessment and Classification
Wound assessment involves evaluating size, depth, and tissue type, while classification categorizes wounds based on severity and characteristics. Accurate documentation is crucial for legal and care continuity. Understanding wound morphology and staging helps guide treatment and predict healing trajectories. Proper classification also aids in differentiating between acute and chronic wounds, such as venous or diabetic ulcers, ensuring targeted interventions.
Classification systems, like the Wagner Ulcer Classification, help standardize wound care approaches; Regular reassessment ensures treatment adjustments, promoting optimal healing outcomes. This process is foundational for effective wound management and patient care, emphasizing precision and consistency in documentation and communication among healthcare providers.
4.2 Principles of Wound Healing and Management
Wound healing progresses through inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases. Effective management involves creating a moist environment, controlling infection, and promoting tissue regeneration. Debridement and dressing techniques are critical for removing necrotic tissue and facilitating healing. Nutritional support and oxygenation also play key roles in optimizing wound repair. Understanding these principles enables healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing complications.
Advanced therapies, such as negative pressure wound therapy, can accelerate healing in complex cases. Regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment strategies ensure wounds progress toward closure. Proper wound management reduces the risk of chronic wounds and improves quality of life for patients.
Advanced Wound Management Techniques
Advanced wound management incorporates debridement, negative pressure therapy, and bioengineered skin substitutes to promote healing. These techniques address complex wounds, reduce infection risks, and enhance tissue regeneration.
Emerging therapies, such as stem cell applications, further optimize wound care outcomes, offering innovative solutions for chronic and non-healing wounds, improving patient recovery and quality of life.
5.1 Debridement and Infection Control
Debridement is a critical procedure in wound care, involving the removal of dead tissue to promote healing. It can be surgical, autolytic, enzymatic, or mechanical. Proper infection control measures, such as antimicrobial dressings and antiseptics, are essential to prevent wound colonization and sepsis. These techniques are vital for reducing bacterial loads and creating an optimal environment for tissue regeneration.
Mastering debridement and infection control is fundamental for managing chronic and complex wounds effectively, ensuring patient safety and improving clinical outcomes.
5.2 Dressing and Bandaging Techniques
Dressing and bandaging are essential for protecting wounds, promoting healing, and preventing infection. Common dressings include hydrocolloid, alginate, and antimicrobial options, each suited for specific wound types. Bandaging techniques, such as compression and immobilization, enhance wound stability and blood flow. Proper application ensures a moist environment, reduces bacterial colonization, and supports tissue regeneration.
Advanced materials, like foam dressings, are used for complex wounds, while multilayer bandaging addresses venous ulcers effectively.
Specialized Wound Care
Specialized wound care addresses complex conditions like diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers, requiring tailored treatment plans and advanced therapies to promote healing and prevent complications.
6.1 Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers require specialized care due to their complexity and high risk of complications. Proper management involves regular debridement, offloading pressure, and controlling blood glucose levels. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent infection and amputation. Using advanced dressings and topical therapies can enhance healing. Patient education on wound care and lifestyle modifications is also essential for long-term management and prevention.
6.2 Venous and Arterial Ulcer Care
Venous and arterial ulcers require distinct management approaches due to their differing pathophysiology. Venous ulcers benefit from compression therapy and elevation, while arterial ulcers often necessitate improving blood flow through revascularization. Accurate diagnosis involves assessing circulation and tissue perfusion. Regular wound debridement and antimicrobial treatments are essential. Patient education on mobility, smoking cessation, and proper footwear can prevent recurrence and promote healing in both types of ulcers.

Documentation and Legal Aspects
Accurate wound documentation is crucial for legal compliance, patient safety, and continuity of care. It ensures adherence to ethical standards and accountability in wound management practices.
7.1 Importance of Accurate Wound Documentation
Accurate wound documentation is essential for legal compliance, continuity of care, and effective communication among healthcare providers. It ensures precise tracking of wound healing progress, supports reimbursement, and reduces liability risks. Detailed records, including wound type, size, and tissue type, facilitate informed decision-making and improve patient outcomes. Proper documentation also aids in identifying trends and improving quality of care, making it a cornerstone of professional wound management practices.
7.2 Legal and Ethical Considerations in Wound Care
Legal and ethical considerations are crucial in wound care to ensure patient rights and safety. Professionals must adhere to confidentiality, informed consent, and standard treatment protocols. Ethical dilemmas, such as end-of-life care decisions, require balancing patient autonomy with medical obligations. Legal compliance involves accurate documentation and adherence to regulations, preventing malpractice claims. Understanding these principles is vital for maintaining trust and delivering high-quality, patient-centered care.
Emerging Trends in Wound Care
Emerging trends in wound care emphasize the role of biotechnology, including stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and innovative dressings like bioactive materials and smart dressings, aiming to enhance healing and improve patient outcomes significantly.
8.1 Role of Biotechnology in Wound Healing
Biotechnology plays a pivotal role in advancing wound healing through innovative therapies like bioactive dressings and growth factors. These technologies stimulate cellular repair and enhance collagen synthesis, promoting faster recovery. Breakthroughs in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine further support complex wound management, offering personalized solutions for chronic and acute injuries, thus improving patient outcomes and reducing complications.
8.2 Stem Cell Therapy and Tissue Engineering
Stem cell therapy and tissue engineering are revolutionizing wound care by promoting tissue regeneration. Stem cells differentiate into specialized cells, accelerating healing. Engineered skin substitutes and bioactive scaffolds provide structural support, enhancing wound closure. These technologies reduce healing times, minimize scarring, and improve outcomes for chronic wounds, offering promising advancements in personalized wound management and regenerative medicine.
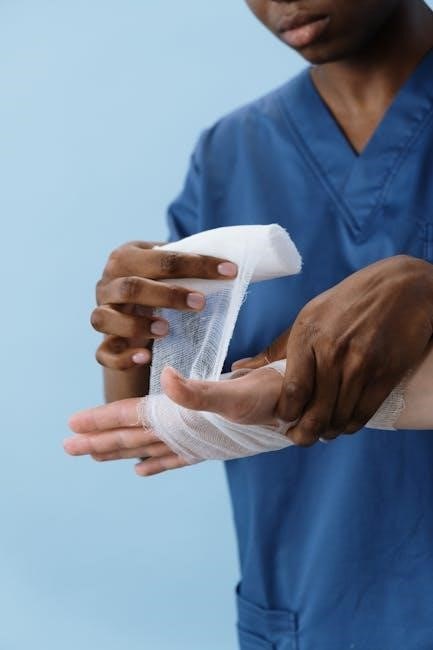
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Case studies provide real-world examples of wound care challenges, offering insights into effective management strategies. Practical applications demonstrate evidence-based approaches for treating various wound types, enhancing clinical decision-making skills.
9.1 Real-World Examples of Wound Care Challenges
Case studies highlight common wound care challenges, such as managing diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries. Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of accurate assessment, timely intervention, and personalized treatment plans. These scenarios also emphasize the need for infection control, proper documentation, and interdisciplinary collaboration to improve patient outcomes and prevent complications.
9.2 Successful Outcomes in Wound Management
Successful wound management often involves effective treatment plans tailored to patient needs. Examples include rapid healing of diabetic foot ulcers through debridement and offloading, or improved venous ulcer closure rates with compression therapy. Proper documentation and interdisciplinary collaboration also play key roles in achieving positive outcomes. These successes highlight the importance of evidence-based practices and skilled healthcare providers in optimizing wound care results.
Wound care certification remains a cornerstone of advanced patient care, driving innovation and improved outcomes. Future directions include integrating biotechnology and stem cell therapy, ensuring continuous professional growth and evidence-based practices.
10.1 The Evolution of Wound Care Certification
Wound care certification has evolved significantly, reflecting advancements in medical science and clinical practices. Initially focused on foundational wound management, it now encompasses specialized areas like diabetic care and infection control, adapting to emerging therapies and technologies.
This growth underscores the certification’s critical role in standardizing wound care practices, ensuring professionals stay updated on evidence-based methodologies and innovative treatments, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and care quality.
10.2 Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education is essential for wound care professionals to stay updated on advancements and maintain certification. Lifelong learning ensures adaptability to new technologies and methodologies, fostering improved patient outcomes and career growth.
Professional development through workshops, courses, and study guides equips practitioners with cutting-edge knowledge, from debridement techniques to biotherapy applications, ensuring they remain proficient in evidence-based wound care practices.